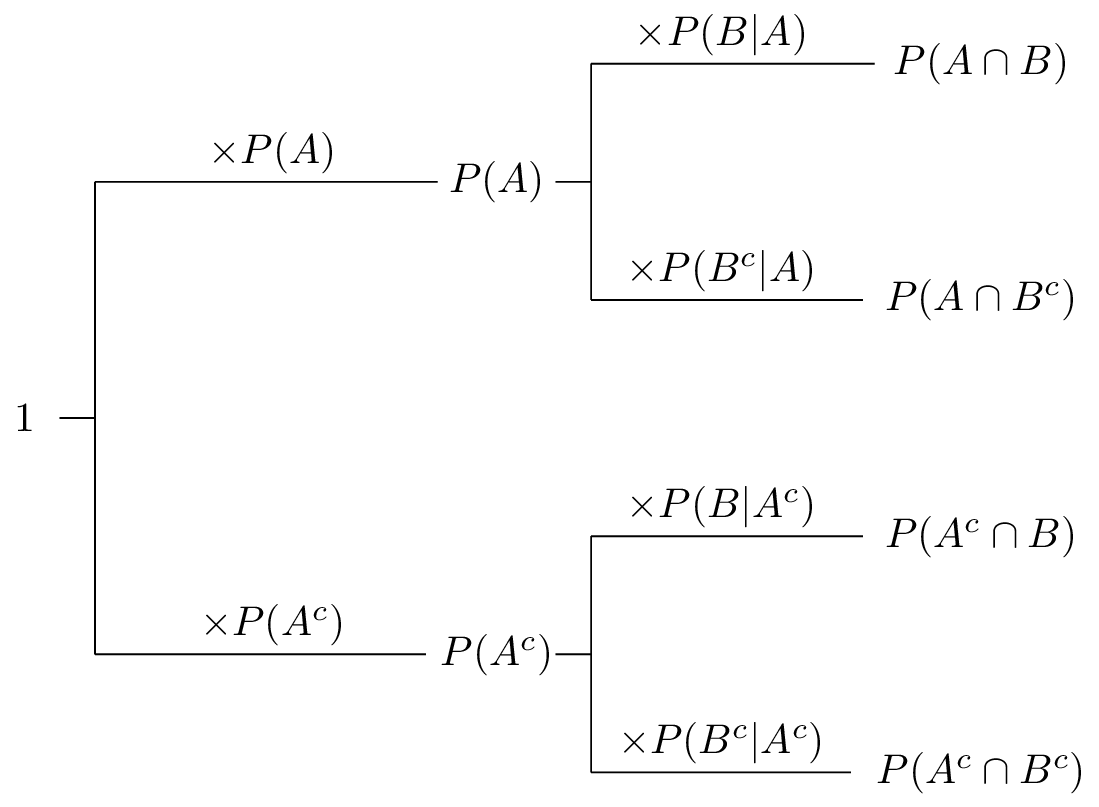12 How to Calculate the Probability of Independent Events P(A or B ) = P(A) + P(B) P(A and B) Depen - YouTube
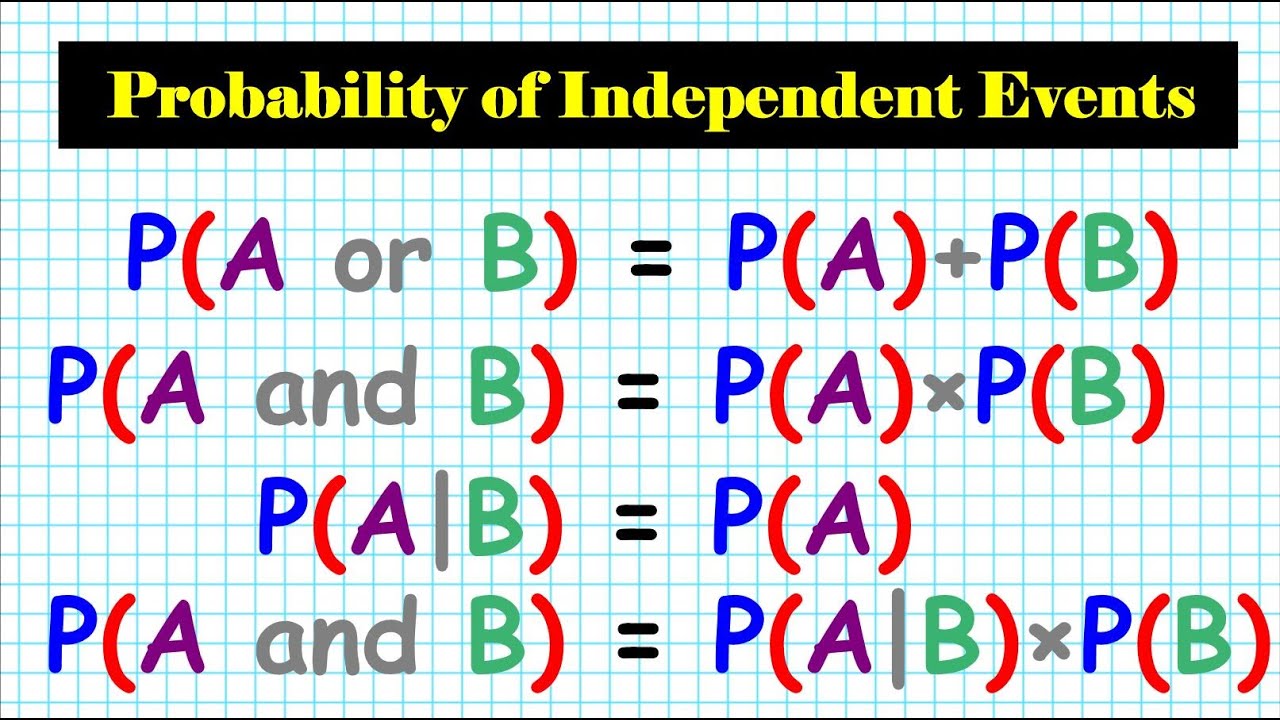
12 How to Calculate the Probability of Independent Events P(A or B ) = P(A) + P(B) P(A and B) Depen - YouTube
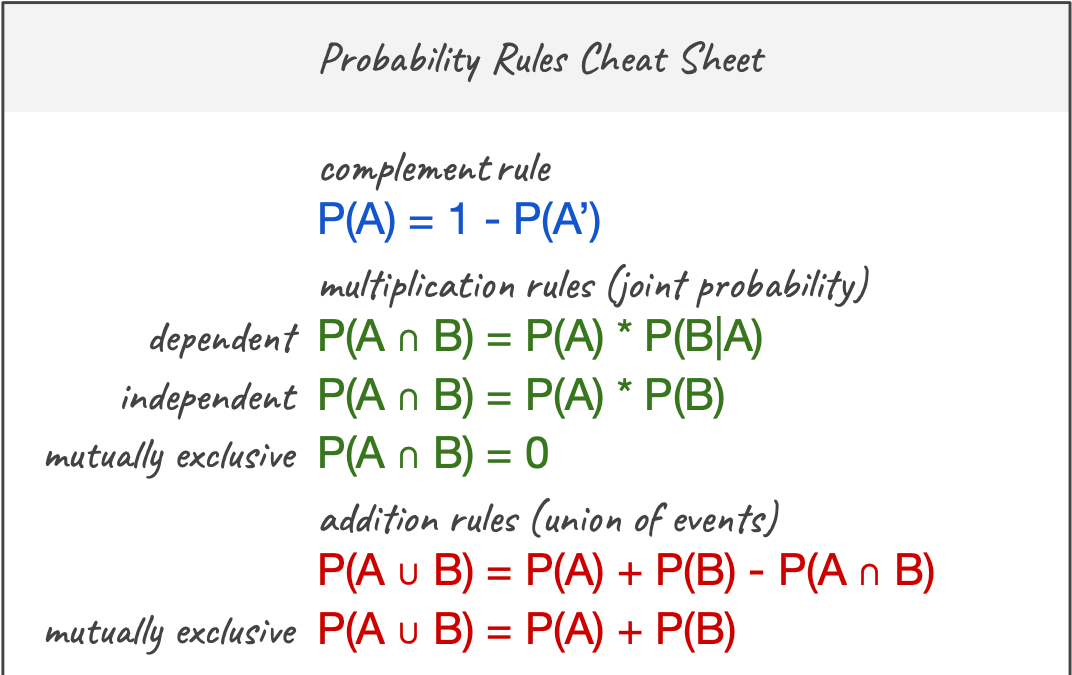
Probability Rules Cheat Sheet. Basic probability rules with examples… | by rita | Data Comet | Medium
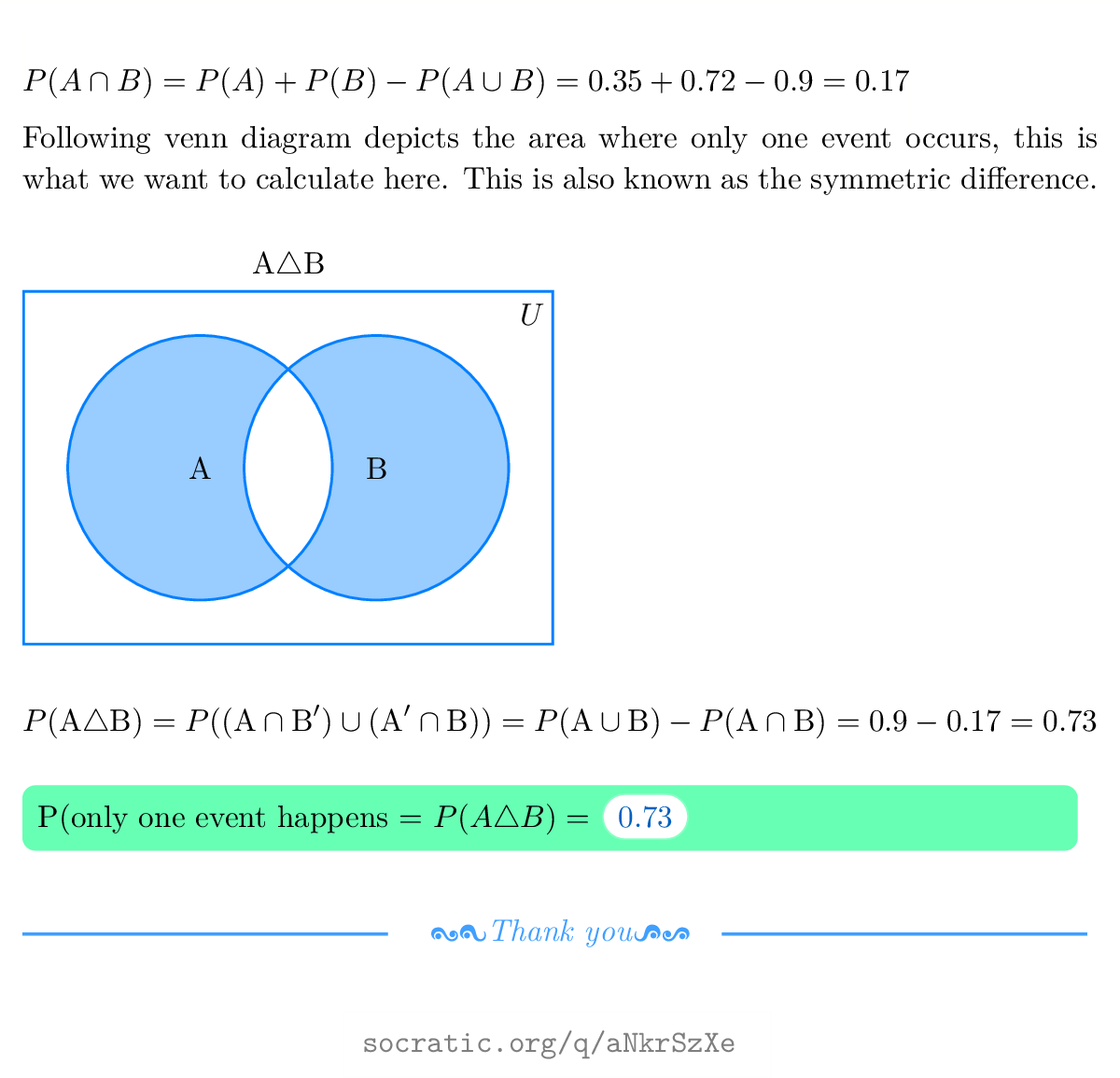
Two events A and B are investigated: P(A)=0.35, P(B)=0.72, the percent chance that at least one of event A or B occur is 90%; What is the probability that only one of

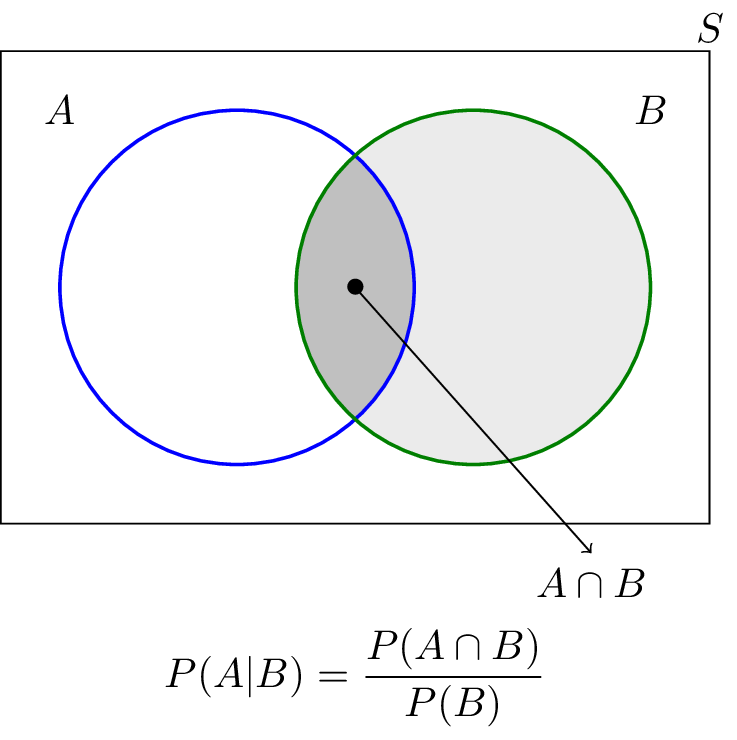
Let A and B be two events such that P(A) = 0.6, P(B) = 0.2 and P(A/B) = 0.5, then find P ( A^ /B^ ) .